The village of Yamakoshi, nestled in the Niigata mountains of Japan, has found a creative way to support its development and sustain its ageing population using NFTs. The Neo-Yamakoshi Village project, started in 2021, has attracted 1,700 “digital citizens” who purchased Nishikigoi NFTs, raising over $423,000. This innovative approach combines digital assets and decentralized governance to tackle challenges faced by rural communities in Japan, according to a report by the Yuri Group.
NFTs and Digital Governance
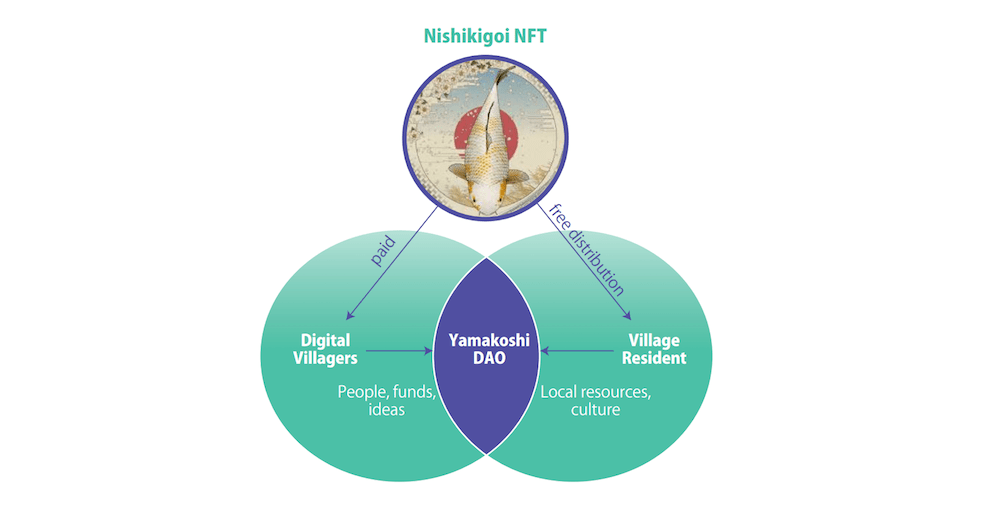
The Nishikigoi NFT collection, named after the colourful breed of koi carp, serves as an identifier for Yamakoshi’s digital citizens and a governance token. These tokens enable participation in the village’s decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), allowing global supporters to influence the community’s decisions. This form of digital governance ensures that even those far from Yamakoshi can contribute to its future.
This initiative supports local activities and strengthens the bond between the village and its digital citizens. It shows how digital tools can foster real-world community engagement and support. Proceeds from the NFT sales have been used for various community initiatives. One notable project was organizing a sports day for local school children, bringing physical and digital residents together.
Financial Impact and Community Projects
Since its inception, the Neo-Yamakoshi Village project has raised significant funds by selling Nishikigoi NFTs, with a floor price of 0.0318 ETH as of June 26. These funds have been crucial in supporting local projects and improving the quality of life for the village’s residents.
The Japanese government has recognized the potential of this initiative, providing support and considering it a model for other rural communities facing similar challenges.
The project’s success has led to discussions about expanding its scope to other municipalities in Japan. If this strategy works and develops, rural Japan could raise sums in the region of half a billion dollars while also pioneering new social technologies with global appeal.

Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its successes, the Neo-Yamakoshi Village project faces several challenges. Older residents often need help with technology, and due to the project’s international scope, there are communication barriers. Additionally, voter turnout in DAO elections has been relatively low, highlighting the difficulty of integrating digital governance frameworks into traditional community settings.
The global NFT markets have seen a downturn, with trading volumes dropping significantly. The second quarter of 2024 is projected to close down 45% compared to previous periods. However, Japan’s cultural tradition of collecting tokens may help maintain the business case for NFTs, providing a resilient market for such initiatives. Observers have noted that Japan’s unique cultural heritage, mainly the Nishikigoi koi carp, adds a compelling story to the NFTs, enhancing their appeal.
Furthermore, Yamakoshi’s initiative fits neatly into Prime Minister Kishida Fumio’s digital transformation (DX) policy to revitalize the nation’s economy.
Final Thoughts
By focusing on the global appeal of traditional Japanese culture and digitizing it, the Neo-Yamakoshi Village project opens access to anyone with an internet connection. This includes NFTs to raise funds and a digital cooperative that netizens can join to play a role in local decision-making.
The Neo-Yamakoshi Village project shows how modern Web3 technologies can address socio-economic issues in rural Japan. By combining NFTs, DAOs, and the global digital community, Yamakoshi is preserving its unique cultural heritage and creating a sustainable future for its residents.